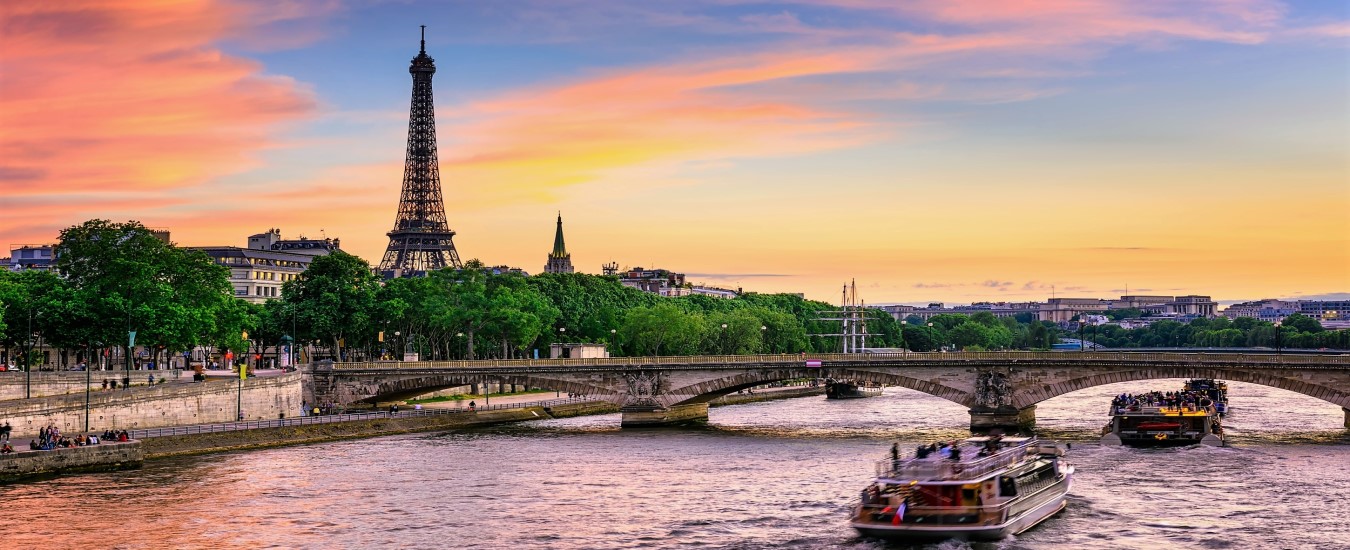
North America
& Caribbean |

South America
|

Africa
|
Asia
|
Europe
|
Australia &
Oceania |

Country Rankings
|

Beyond
Earth |
|
mail
ContactUs
|
|
info
AboutUs
|
Flag
National anthem

Coat of arms
Country location map
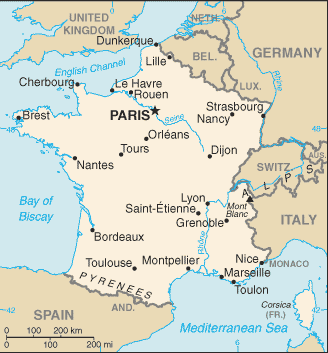
Country static map
Country dynamic (scrollable) map
Current weather & time
-
infoGeneral informationkeyboard_arrow_up
- Country common name: France
- Country official name: French Republic (Republique francaise)
- Continent: Europe
- 3-Letter abbreviation: FRA
- 2-Letter abbreviation: FR
- Capital: Paris
- Major cities: 11.017 million PARIS (capital), 1.719 million Lyon, 1.608 million Marseille-Aix-en-Provence, 1.063 million Lille, 1.024 million Toulouse, 969,000 Bordeaux
- Currency: Euro (click for current conversion rates)
- Languages: French (official) 100%, declining regional dialects and languages (Provencal, Breton, Alsatian, Corsican, Catalan, Basque, Flemish, Occitan, Picard)
- Motto: "Liberty, equality, fraternity"
- National holiday(s): Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790) - although often incorrectly referred to as Bastille Day, the celebration actually commemorates the holiday held on the first anniversary of the storming of the Bastille (on 14 July 1789) and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy; other names for the holiday are Fete Nationale (National Holiday) and quatorze juillet (14th of July)
flagGovernmentkeyboard_arrow_up- Chief of state: President Emmanuel MACRON (since 14 May 2017)
- Head of government: Prime Minister Francois BAYROU (since 13 December 2024)
- Government type: semi-presidential republic
insert_photoCountry notes & photographskeyboard_arrow_up{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"France"},{"insert":", officially the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French Republic"},{"insert":", is a country primarily located in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Western Europe"},{"insert":", consisting of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"metropolitan France"},{"insert":" and several "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"overseas regions"},{"insert":" and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"territories"},{"insert":". The metropolitan area of France extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. The overseas territories include "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French Guiana"},{"insert":" in South America and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"several islands"},{"insert":" in the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Atlantic"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Pacific "},{"insert":"and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Indian Oceans"},{"insert":". France borders Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany to the northeast, Switzerland, Monaco and Italy to the east, Andorra and Spain to the south, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. The country's eighteen integral regions (five of which are situated overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km"},{"attributes":{"script":"super"},"insert":"2"},{"insert":" (248,573 sq mi) and a total population of 67.8 million. France is a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"unitary semi-presidential republic"},{"insert":" with its capital in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Paris"},{"insert":", the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial center. Other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice. France, including its overseas territories, has the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"most time zones"},{"insert":" of any country, with a total of twelve.\n\nDuring the Iron Age, what is now metropolitan France was inhabited by the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Gauls"},{"insert":". The area was annexed by "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Rome"},{"insert":" in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"51 BC"},{"insert":", developing a distinct "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Gallo-Roman culture"},{"insert":" that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks arrived in 476 and formed the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Kingdom of Francia"},{"insert":", which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Kingdom of France"},{"insert":" in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"987"},{"insert":".\n\nIn the High Middle Ages, France was a highly decentralized feudal kingdom in which the authority of the king was barely felt. King Philip Augustus achieved remarkable success in the strengthening of royal power and the expansion of his realm, doubling its size and defeating his rivals. By the end of his reign, France had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. In the mid-14th century, French monarchs were embroiled in a series of dynastic conflicts with their English counterparts, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, from which they ultimately emerged victorious. Disputes with Spain and the Holy Roman Empire soon followed during the Renaissance. Meanwhile, French culture flourished and a global colonial empire was established, which by the 20th century would become the second largest in the world. The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots), which severely weakened the country. But France once again emerged as Europe's dominant cultural, political, and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War. Despite the wealth of the nation, an inadequate financial model and inequitable taxation system coupled with endless and costly wars meant that the kingdom was left in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. Especially costly were the Seven Years' War and American War of Independence. \n\nThe "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French Revolution"},{"insert":" in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1789"},{"insert":" saw the fall of the absolute monarchy that characterized the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Ancien Régime"},{"insert":" and from its ashes, rose one of modern history's earliest republics, which drafted the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The declaration expresses the nation's ideals to this day. Following the revolution, France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Napoleon Bonaparte"},{"insert":", subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of European and world history. After the collapse of the empire and a relative decline, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments culminating in the establishment of the French Third Republic in 1870 in the midst of the Franco-Prussian War. France was one of the prominent participants of World War I, from which it emerged victorious, and was one of the Allied powers in World War II, but came under occupation by the Axis in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Fifth Republic"},{"insert":", led by "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Charles de Gaulle"},{"insert":", was formed in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1958 "},{"insert":"and remains to this day. Algeria and nearly all other French colonies became independent in the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1960s"},{"insert":", with most retaining close economic and military connections with France.\n\nFrance retains its centuries-long status as a global center of art, science, and philosophy. It hosts the world's "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"fifth-largest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites"},{"insert":" and is the leading tourist destination, receiving over "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"89 million foreign visitors"},{"insert":" in 2018. France is a developed country with the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the ninth-largest by PPP. In terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world. France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, and human development. It remains a great power in global affairs, being one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. France is a founding and leading member of the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"European Union"},{"insert":" and the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Eurozone"},{"insert":", and a member of the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Group of 7"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD"},{"insert":"), the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"World Trade Organization (WTO)"},{"insert":", and "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"La Francophonie"},{"insert":".\n\nAlthough ultimately a victor in World Wars I and II, France suffered extensive losses in its empire, wealth, manpower, and rank as a dominant nation-state. Nevertheless, France today is one of the most modern countries in the world and is a leader among European nations. Since 1958, it has constructed a presidential democracy resistant to the instabilities experienced in earlier parliamentary democracies. In recent years, its reconciliation and cooperation with Germany have proved central to the economic integration of Europe, including the introduction of a common exchange currency, the euro, in January 1999. At present, France is at the forefront of efforts to develop the EU's military capabilities to supplement progress toward an EU foreign policy.\n"}]}terrainGeographic informationkeyboard_arrow_up- Surface area (in km²): 643,801
- Highest point: Mont Blanc 4,810
- Neighboring countries: Andorra 55 km, Belgium 556 km, Germany 418 km, Italy 476 km, Luxembourg 69 km, Monaco 6 km, Spain 646 km, Switzerland 525 km
- Neighboring seas and oceans: None
- Climate: metropolitan France
radioRadio stationskeyboard_arrow_upsupervised_user_circlePopulationkeyboard_arrow_up- Population: 67,848,156
- Population density (inhabitants per km²): 105.4
- Average age (in years): 41.7
- Life expectancy at birth (in years): 82.2
- Ethnicity: Celtic and Latin with Teutonic, Slavic, North African, Indochinese, Basque minorities
- Gross domestic product (GDP) per inhabitant (in US dollars): 44,100
- Cultural practices: Hugging is a much less common form of greeting in France than in other countries, and may be received uncomfortably.
local_diningPopular food & drinkskeyboard_arrow_up{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true,"link":"https://www.cyberspace23.com/recipe-display.php?id=44"},"insert":"French onion soup"},{"insert":" is a type of soup usually based on "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"meat stock"},{"insert":" and "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"onions"},{"insert":", and often served gratinated with "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"croutons "},{"insert":"or a larger piece of bread covered with cheese floating on top. Although ancient in origin, the dish underwent a resurgence of popularity in the 1960s in the United States due to a greater interest in French cuisine. French onion soup may be served as a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"meal"},{"insert":" in itself or as a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"first course"},{"insert":". Onion soups have been popular at least as far back as Roman times. Throughout history, they were seen as food for poor people, as onions were plentiful and easy to grow. The modern version of this soup originated in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Paris"},{"insert":", France in the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"18th century"},{"insert":", made from beef broth, and caramelized onions.\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Escargot"},{"insert":", from the French word for "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"snail"},{"insert":", is a dish consisting of "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"cooked land snails"},{"insert":". It is often served as an "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"hors d'oeuvre"},{"insert":" and is common in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"France "},{"insert":"and parts of India. Escargot is part of the typical cuisines of Cyprus, Malta, Crete, areas of mainland Greece, as well as the North African countries Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco. Escargot is consumed in Germany, Great Britain, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. Not all species of land snail are edible, and many are too small - not worthwhile to prepare and cook them. Among the edible species, the palatability of the flesh varies. In "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"France"},{"insert":", the species eaten most often is "},{"attributes":{"italic":true,"bold":true},"insert":"Helix pomatia"},{"insert":". The \""},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"petit-gris"},{"insert":"\" "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Cornu aspersa"},{"insert":" and "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Helix lucorum"},{"insert":" are also eaten. Several additional species, such as "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Elona quimperiana"},{"insert":", are popular in Europe.\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Roquefort"},{"insert":" is a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"sheep milk cheese"},{"insert":" from "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Southern France"},{"insert":", and is one of the world's best known "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"blue cheeses"},{"insert":". Though similar cheeses are produced elsewhere, the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"European Union (EU"},{"insert":") law dictates that only those cheeses aged in the natural"},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":" Combalou caves"},{"insert":" of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Roquefort-sur-Soulzon"},{"insert":" may bear the name Roquefort, as it is a recognized geographical indication, or has a protected designation of origin. The cheese is "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"white"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"tangy"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"crumbly "},{"insert":"and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"slightly mois"},{"insert":"t, with distinctive veins of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"blue mold"},{"insert":". It has a characteristic fragrance and flavor with a notable taste of "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"butyric acid"},{"insert":"; the blue veins provide a sharp tang. It has no rind; the exterior is edible and slightly salty. A typical wheel of Roquefort weighs between 2.5 and 3 kg (6 and 7 lb), and is about 10 cm (4 in) thick. Each kilogram of finished cheese requires about 4.5 liters (about 1 USA gal) of milk to produce. In France, Roquefort is often called the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"\"King of Cheeses\""},{"insert":" or the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"\"Cheese of Kings\""},{"insert":", although those names are also used for other cheeses. Photo credit: Dominik Hundhammer.\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Champagne"},{"insert":" is a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"sparkling wine"},{"insert":" originated and produced in the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Champagne wine region"},{"insert":" of France under the rules of the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"appellation"},{"insert":", that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, specific grape-pressing methods and secondary fermentation of the wine in the bottle to cause carbonation. The grapes "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Pinot noir"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Pinot meunier"},{"insert":", and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Chardonnay"},{"insert":" are used to produce almost all Champagne, but small amounts of Pinot blanc, Pinot gris (called Fromenteau in Champagne), Arbane, and Petit Meslier are vinified as well. Champagne became associated with "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"royalty "},{"insert":"in the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"17th"},{"insert":", "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"18th"},{"insert":", and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"19th centuries"},{"insert":". The leading manufacturers made efforts to associate their Champagnes with nobility and royalty through advertising and packaging, which led to its popularity among the emerging middle class.\n"}]}
local_post_officePostage stampskeyboard_arrow_up{"ops":[{"insert":"The first stamps of France were issued on 1 January "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1849"},{"insert":". They were designed by Jacques-Jean Barre. The medallion depicts the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"head of goddess Ceres"},{"insert":" facing left. In 1852 a new series of definitive stamps were issued, retaining the inscription \"REPUB FRANC\" but replacing Ceres with the head of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"insert":"In "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1853"},{"insert":", after proclamation of the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"2nd Empire"},{"insert":", the inscription was changed to "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"\"EMPIRE FRANC\""},{"insert":", while retaining the head of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Napoleon III"},{"insert":" in the medallion.\nStarting in 1862, a new type of definitive stamp was introduced. It depicts the head of Napoleon III with a laurel wreath and the inscription changed to "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"\"EMPIRE-FRANCAIS\""},{"insert":". The Napoleon stamps remained in use until the fall of the 2nd Empire in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1870"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"insert":"The above "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"2010"},{"insert":" stamp commemorates the 100th Anniversary of the First Flight by Seaplane by Henri Fabre "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Henri Fabre"},{"insert":" (29 November 1882 - 30 June 1984) was a French aviator and the inventor of the first successful seaplane, the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Fabre Hydravion"},{"insert":". Henri Fabre was born into a prominent family of shipowners in the city of Marseille. He was educated in the Jesuit College of Marseilles where he undertook advanced studies in sciences. He intensively studied aeroplane and propeller designs. He patented a system of flotation devices which he used when he succeeded in taking off from the surface of the Etang de Berre on 28 March 1910. On that day, he completed "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"four consecutive flights"},{"insert":", the longest about 600 meters. the "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Hydravion"},{"insert":" has survived and is displayed in the Musee de l'air et de l'espace (English: Air and Space Museum) in Paris. Henri Fabre was soon contacted by Glenn Curtiss and Gabriel Voisin who used his invention to develop their own seaplanes. As late as "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1971"},{"insert":", Fabre he was still sailing his own boat single-handedly in Marseille harbor. He died at the age of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"101"},{"insert":" as one of the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"last living pioneers of human flight"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
{"ops":[{"insert":"In "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"2021"},{"insert":" the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French National Center for Space Studies (CNES)"},{"insert":", celebrated its "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"60th anniversary"},{"insert":". The occasion was marked by a commemorative stamp. At 60 year old CNES does not have to be ashamed of its record. When it was created on December 19, "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1961"},{"insert":", the French space agency was little more than a design office set up to complement the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Diamant"},{"insert":" national launchers project. The latter was launched the day before under the aegis of the military, as the culmination of the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Precious Stone program"},{"insert":", the purpose of which is above all to develop French ballistic deterrence technologies. CNES has been cooperating in all directions, placing the agency as an essential partner on the international scene – except in North Korea – to the point of opening outlets for French scientists on the most fascinating missions. An American Martian probe, "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Insight"},{"insert":", was even designed around a French seizmometer. CNES fosters innovation, by supporting both technologies from laboratories and its traditional partners, as well as start-ups.\n"}]}
tap_and_playTelephone & Internet communicationkeyboard_arrow_up- Country international telephone code: +33
- Local emergency telephone number(s): Ambulance: 112, 15; Fire: 112, 18; Police: 112, 17
- Internet code: .fr
- Number of Internet users: 59,926,585
- Percentage of Internet-connected population: 88.3%
gradeAlso useful to knowkeyboard_arrow_up- Vaccinations: For recommendations please refer to the World Health Organization (WHO), or the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) websites.
- Potable/drinkable water: Yes
- International driving permit: Suggested
- Road driving side: Right
-
Electricity/Voltage/Plug type(s):
230 V / 50 Hz / plug type(s): C, E
keyboard_arrow_leftkeyboard_arrow_right10
-
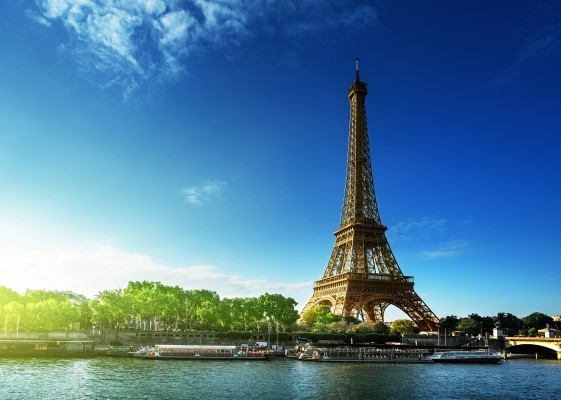

{"ops":[{"insert":"Built for the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1889 World's Fair"},{"insert":" in Paris, the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Eiffel Tower"},{"insert":" is a 1000-foot tall wrought-iron tower, considered an architectural wonder and one of the most recognizable structures on the planet. It underwent a major facelift in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1986"},{"insert":" and is repainted every seven years. It welcomes more visitors than any other paid monument in the world, an estimated 7 million people per year.\n"}]}
-
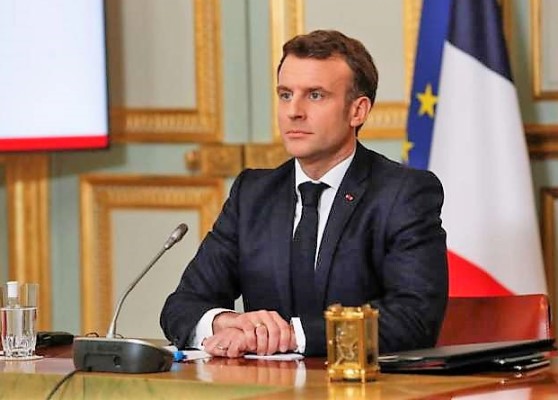

{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Emmanuel Macron"},{"insert":" (born 21 December 1977) is a French politician who has served as "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"President of France"},{"insert":" since "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"2017"},{"insert":". "},{"attributes":{"italic":true},"insert":"Ex officio"},{"insert":", he is also one of the two Co-Princes of Andorra. Prior to his presidency, Macron served as Minister of Economics, Industry and Digital Affairs under President Franasois Hollande between 2014 and 2016.\n"}]}
-

{"ops":[{"insert":"The French "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"National Assembly"},{"insert":" consists of 577 Members of Parliament (MP, also called « députés »). A député represents his/her constituency (une circonscription) which totalled approximately 100,000 inhabitants. 539 députés represent Metropolitan France, 27 overseas départements and territories, and 11 French residents live outside of France. The députés are elected by popular vote to five-year terms\n"}]}
-
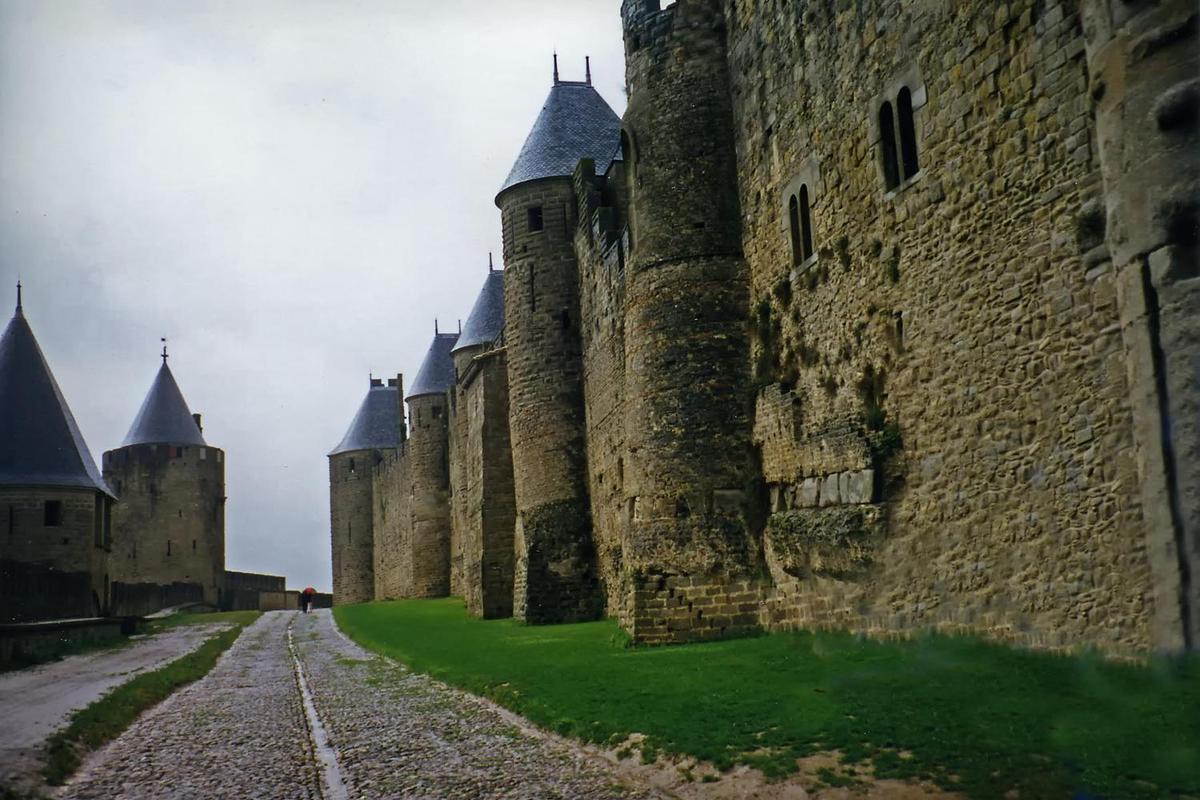

{"ops":[{"insert":"Some of the massive walls at the fortified town of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Carcassone"},{"insert":". Restored in 1853, the fortress became a "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"UNESCO World Heritage Site"},{"insert":" in 1997.\n"}]}
-
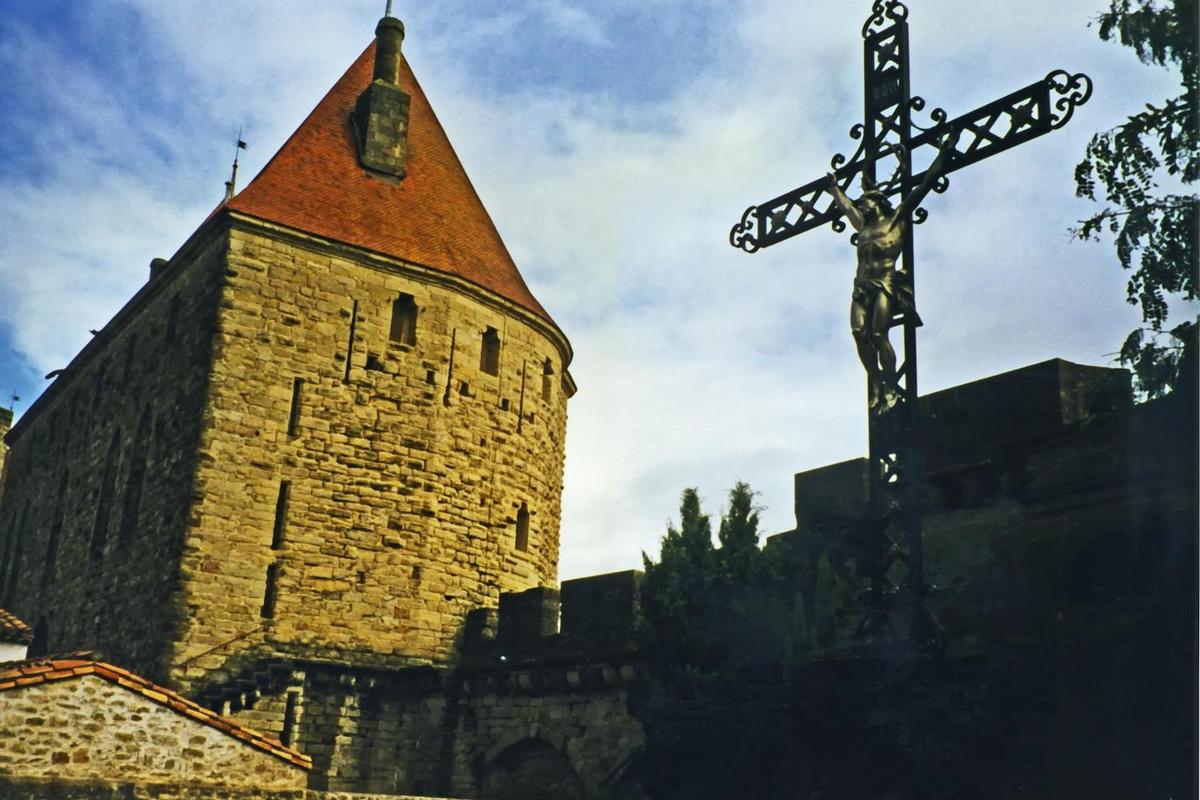

{"ops":[{"insert":"A section of the fortifications at "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Chateau Comtal"},{"insert":", part of the larger defenses at the fortress of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Carcassone"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
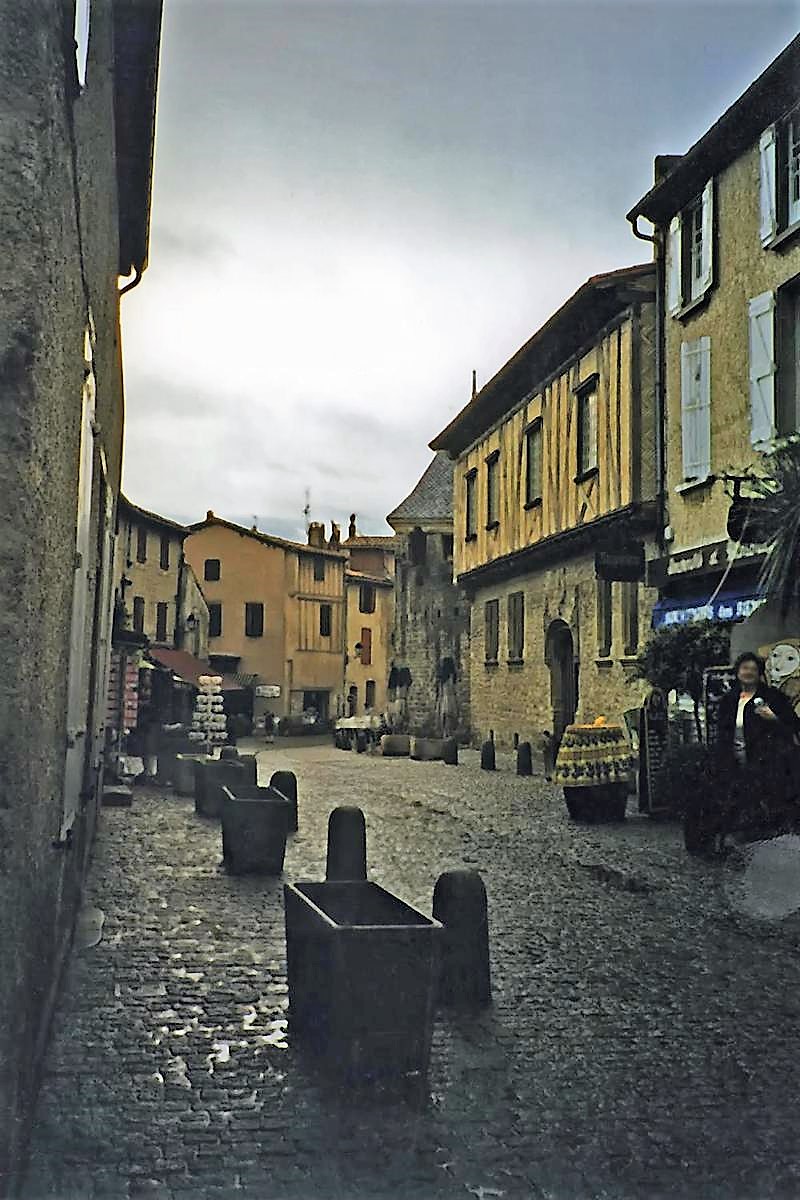

{"ops":[{"insert":"A street scene on a rainy day in the fortified town of"},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":" Carcassone"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
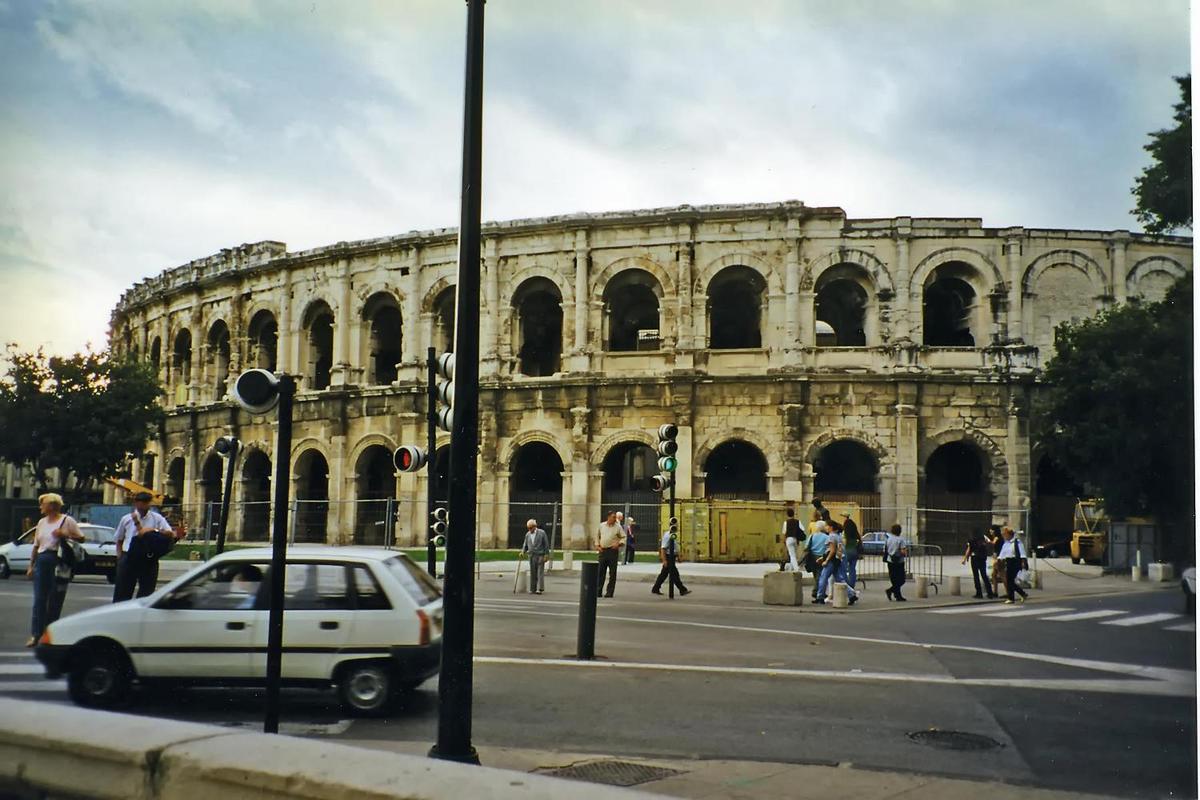

{"ops":[{"insert":"The ancient "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Roman arena"},{"insert":" at "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Nimes"},{"insert":" is still in use today. Built about "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"A.D. 70"},{"insert":", it was remodeled in 1863 and can seat some 16,300 spectators.\n"}]}
-
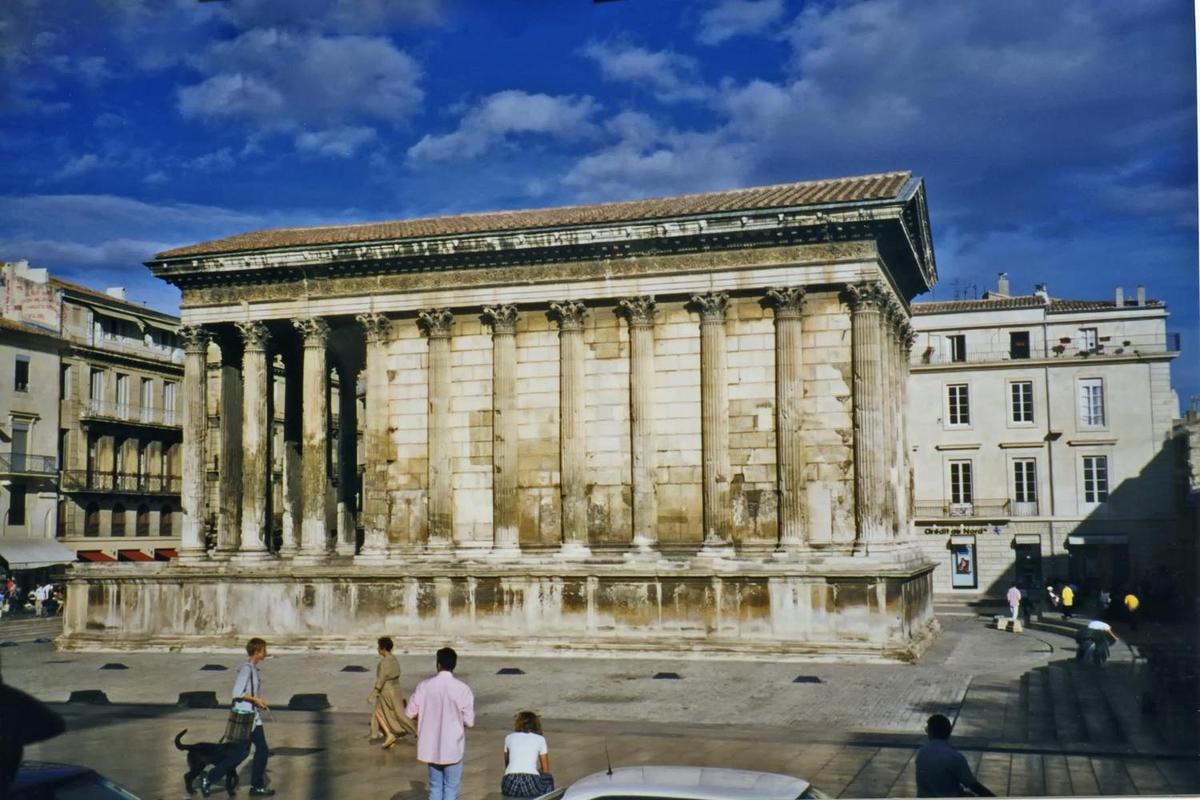

{"ops":[{"insert":"The "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Maison Carree"},{"insert":" in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Nimes"},{"insert":", one of the best preserved of surviving "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Roman temples"},{"insert":", dates to "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"16 B.C"},{"insert":". In subsequent centuries it served as a church, a meeting hall, a storehouse, and a stable. In 1823 it became a museum.\n"}]}
-
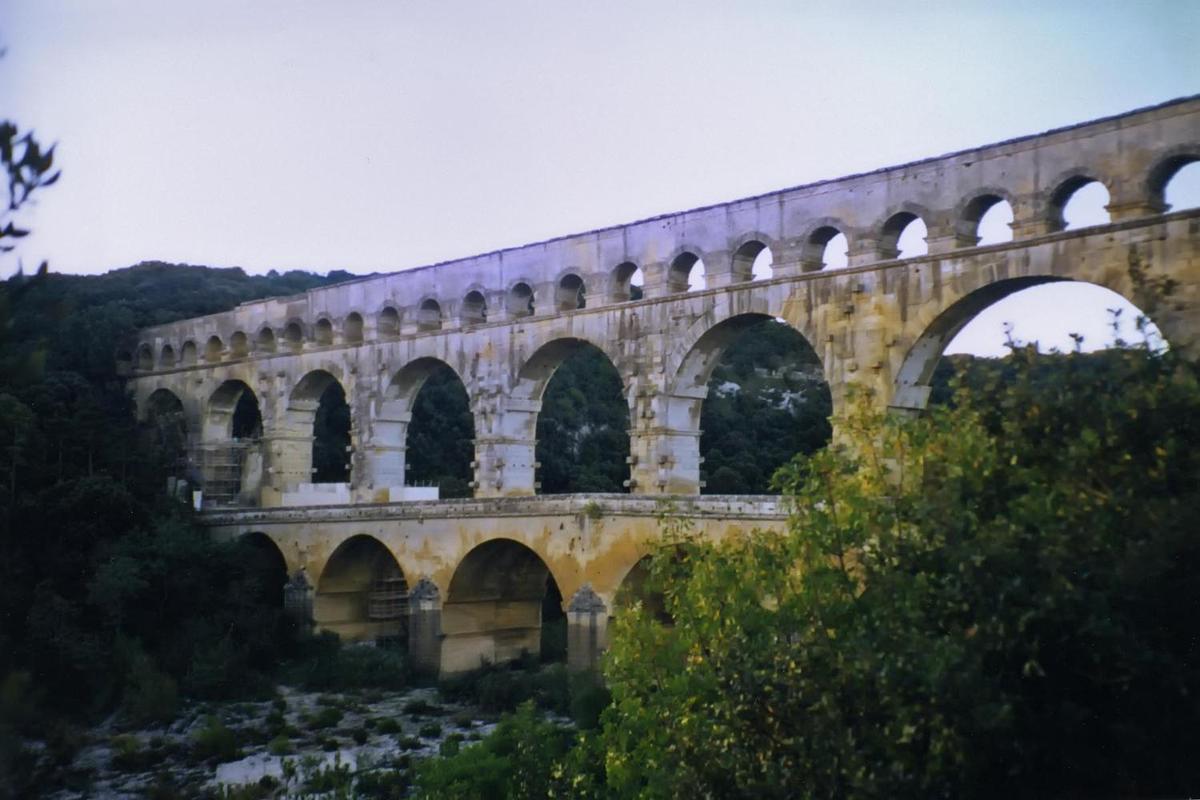

The Roman aqueduct at Pont du Gard, built during the mid-first century A.D., was part of a 50 km (30 mi) long aqueduct system that brought water to the city of Nemausus (today's Nimes). Built entirely without the use of mortar, its construction is thought to have taken about three years using 800 to 1,000 workers.
-
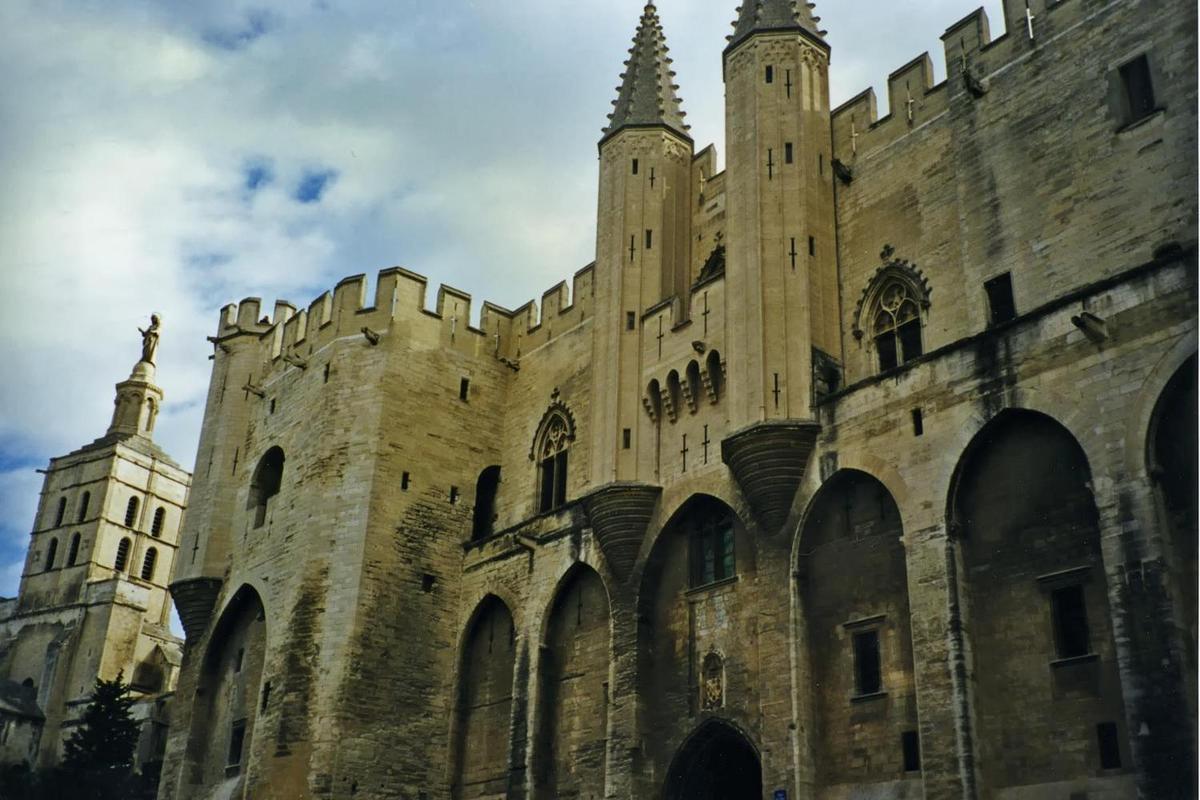

The city of Avignon in southeastern France is well known as the former seat of the papacy in the 14th century. Shown is the Palais des Papes (Palace of the Popes) on the right and the Romanesque Cathedral Notre Dames-des Doms on the far left.
-
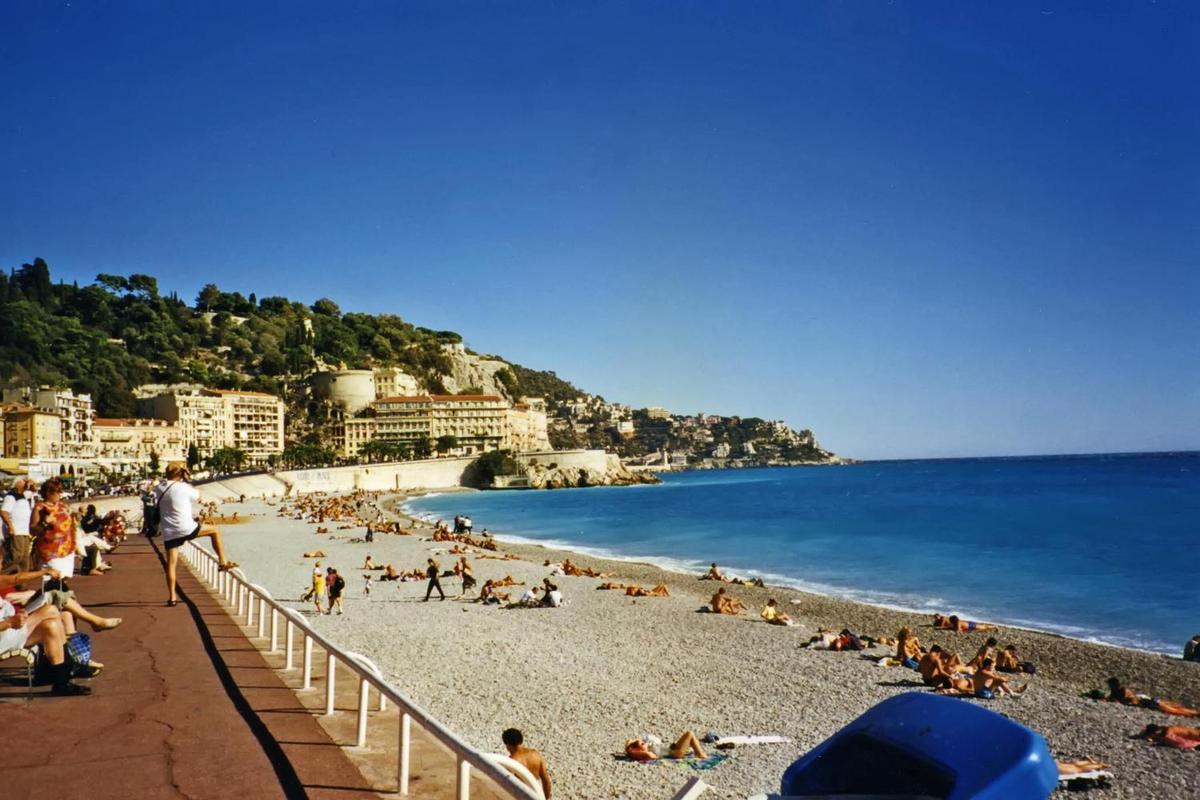

{"ops":[{"insert":"A beach at "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Nice"},{"insert":". The city is a major tourist center and a leading resort along the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French Riviera"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
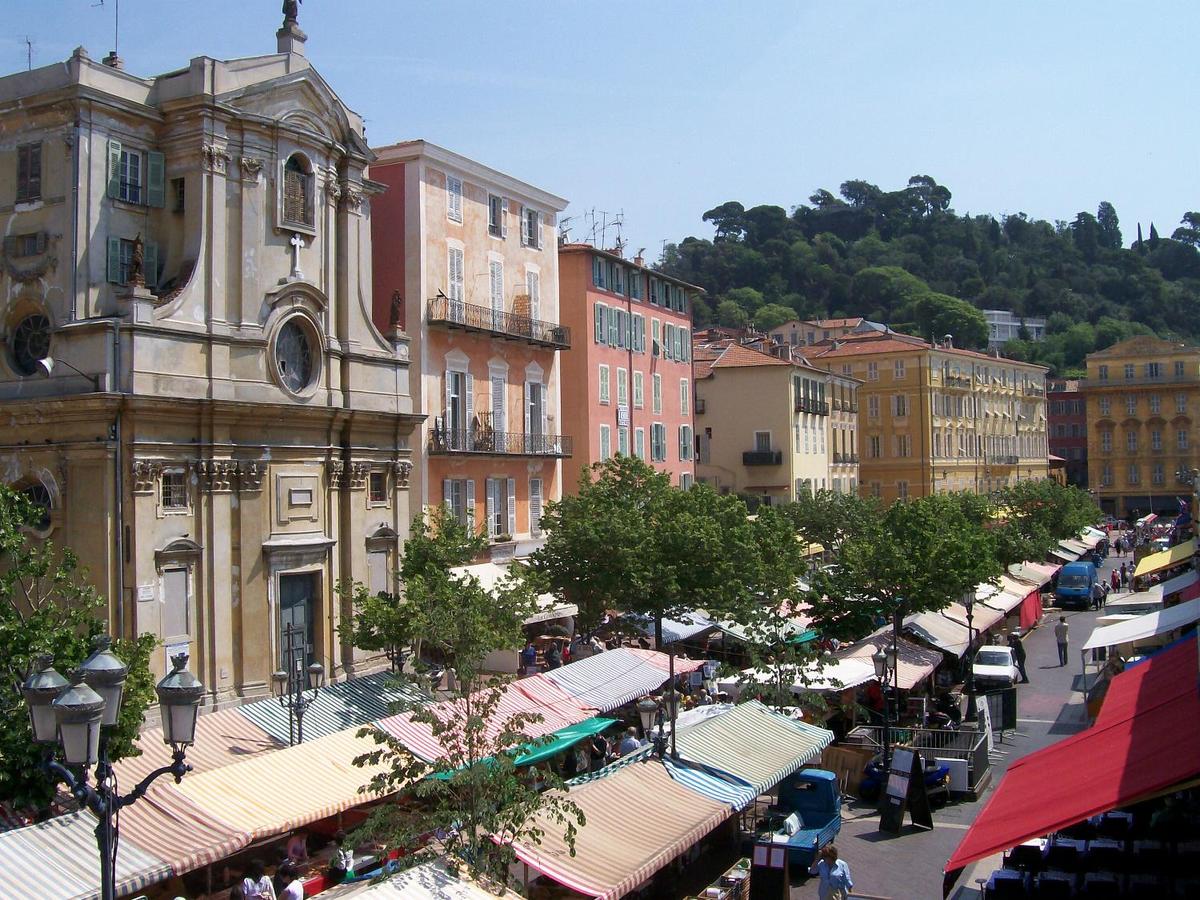

{"ops":[{"insert":"Farmers market in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Nice"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
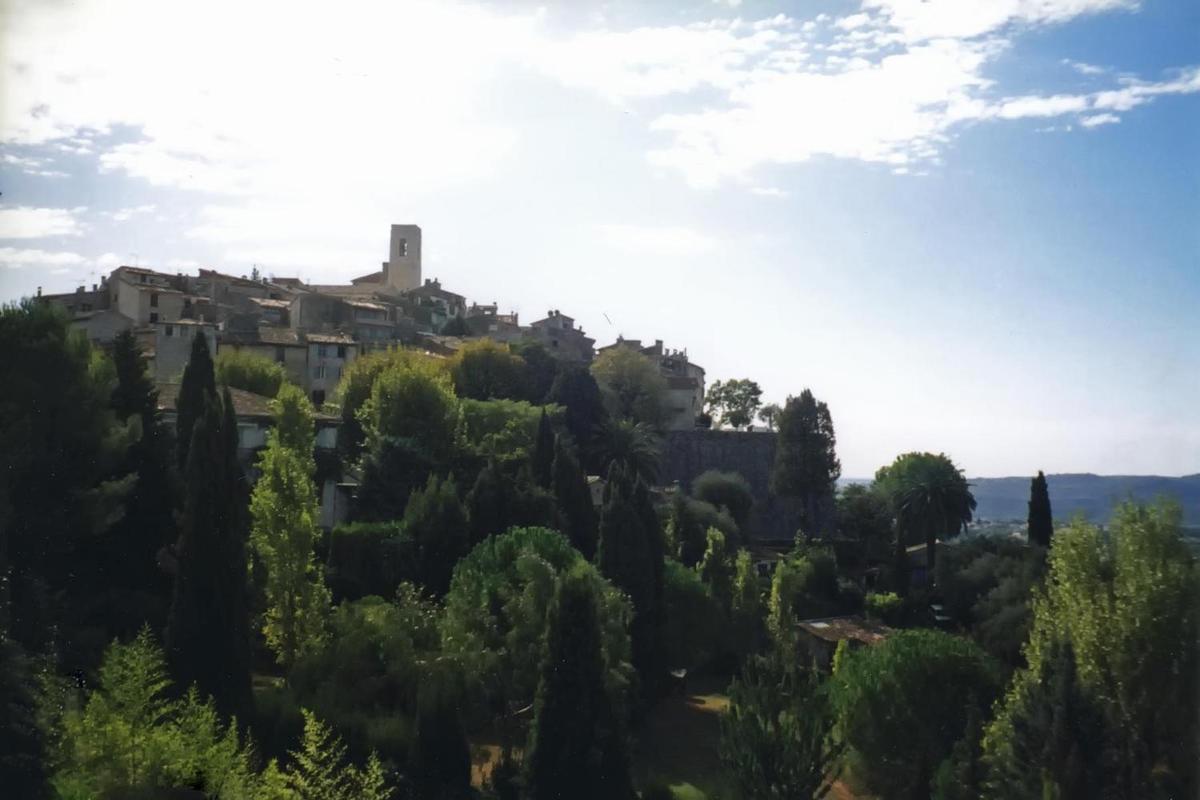

{"ops":[{"insert":"Approaching the fortified medieval town and artist's haven of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Saint-Paul de Vence"},{"insert":" in Provence.\n"}]}
-
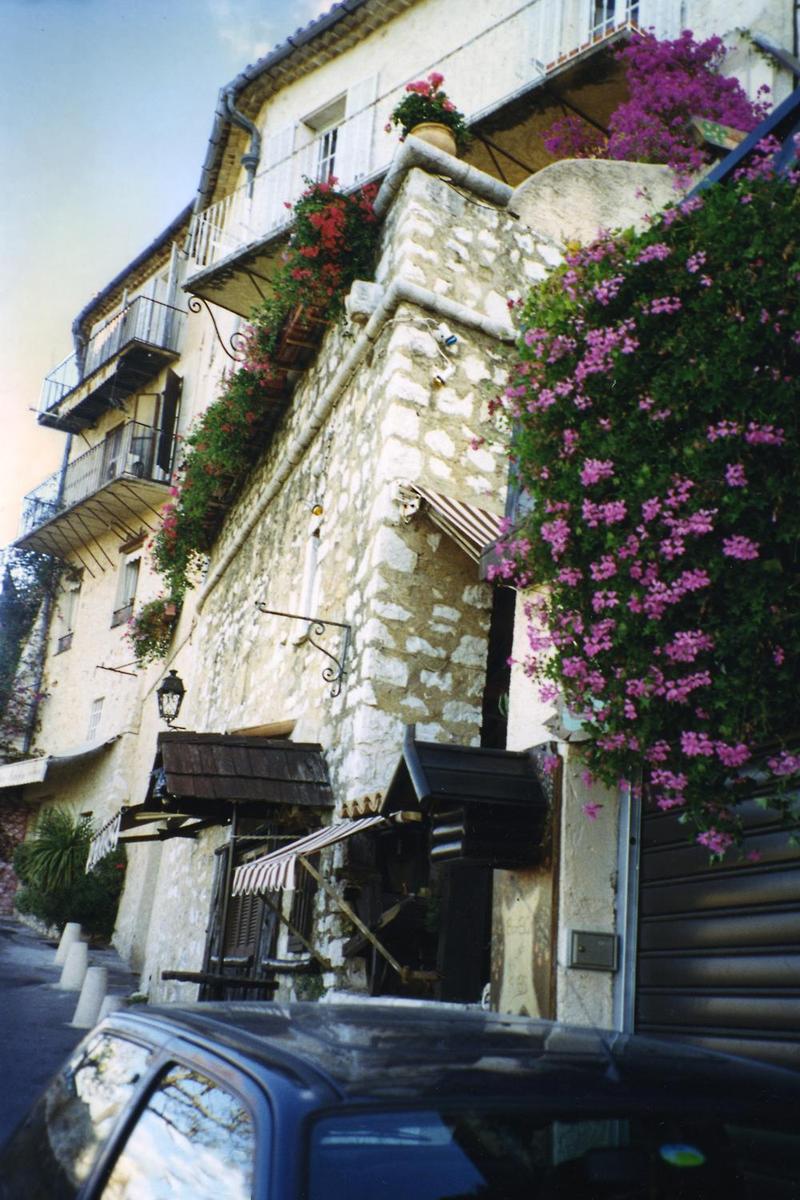

{"ops":[{"insert":"Flowers drip from balconies in the town of "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Saint-Paul de Vence"},{"insert":" in Provence.\n"}]}
-
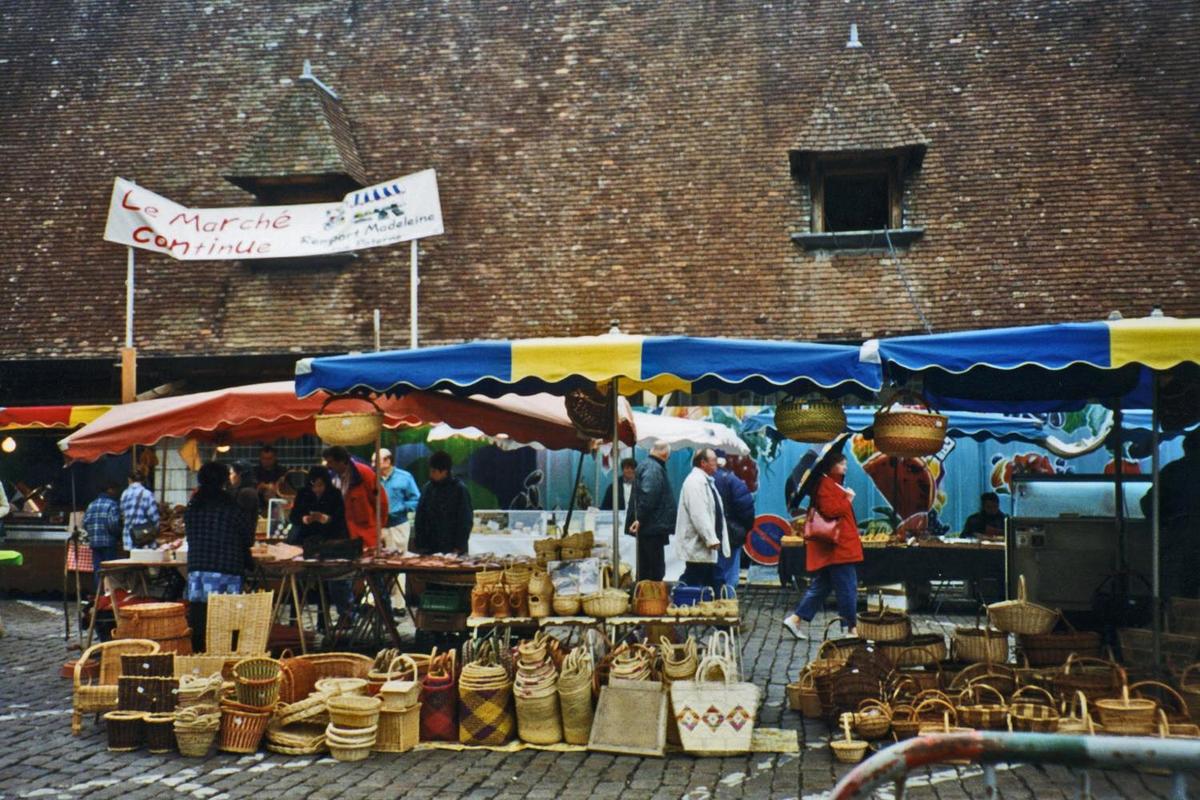

{"ops":[{"insert":"A street market in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Beaune"},{"insert":", a town located in the heart of the Burgundy wine region.\n"}]}
-
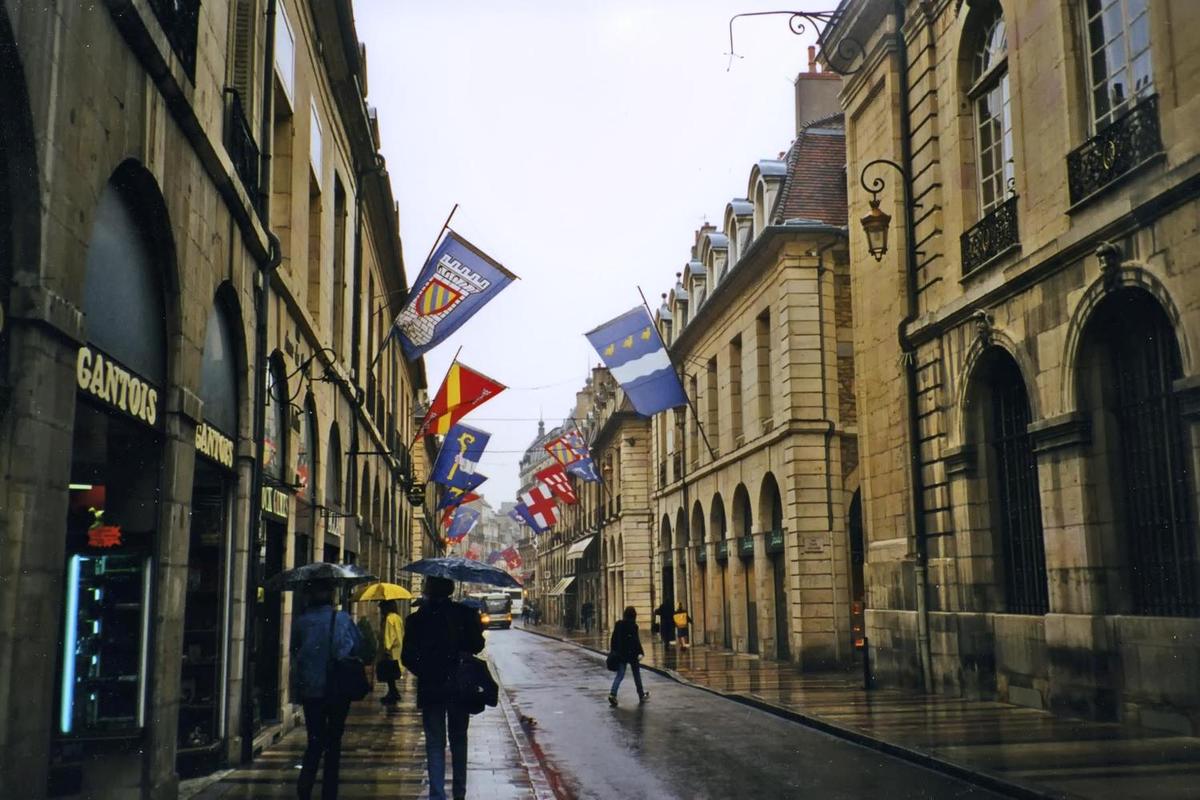

{"ops":[{"insert":"A street scene in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Dijon"},{"insert":", the capital of the Burgundy region. The city was first settled by the Romans and then became the domain of the Dukes of Burgundy, who ruled the area until the late 1400s. It is known for its many architectural styles and hosts the annual Dijon International and Gastronomic Fair.\n"}]}
-
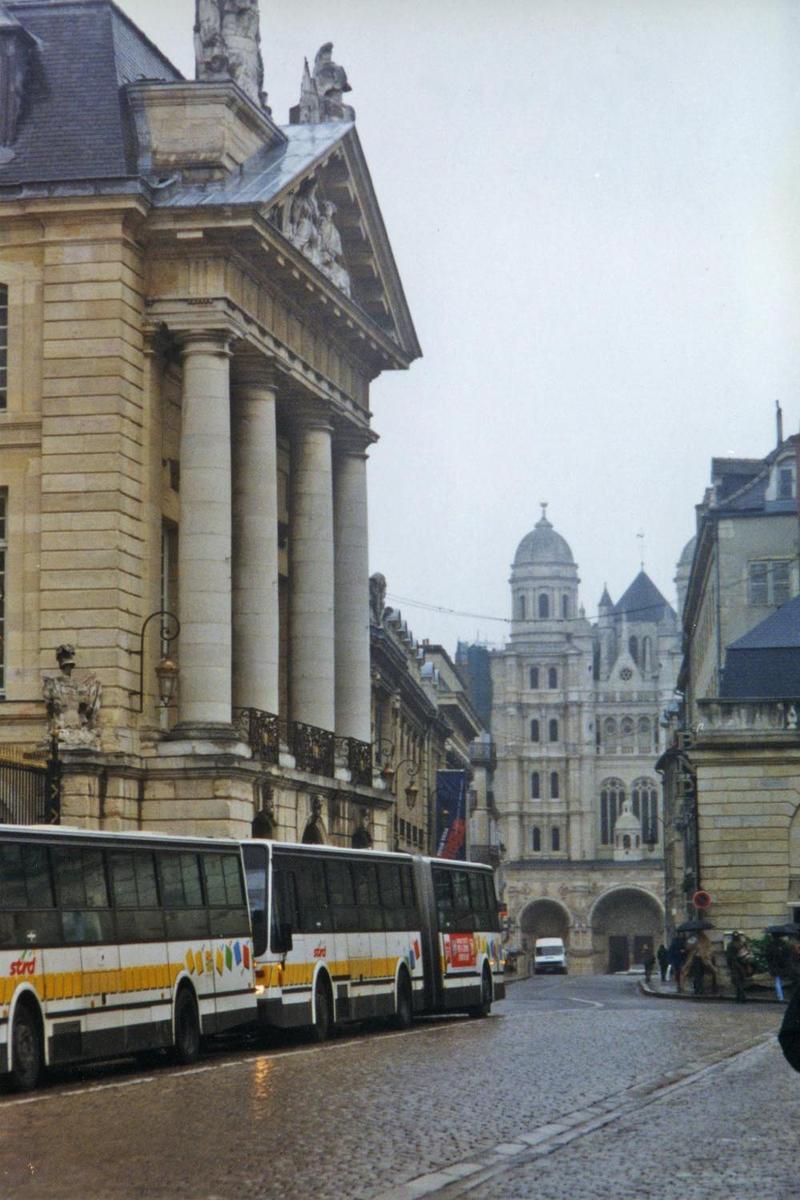

The Palais des Ducs de Bourgogne (Palace of the Dukes of Burgundy) in Dijon.
-
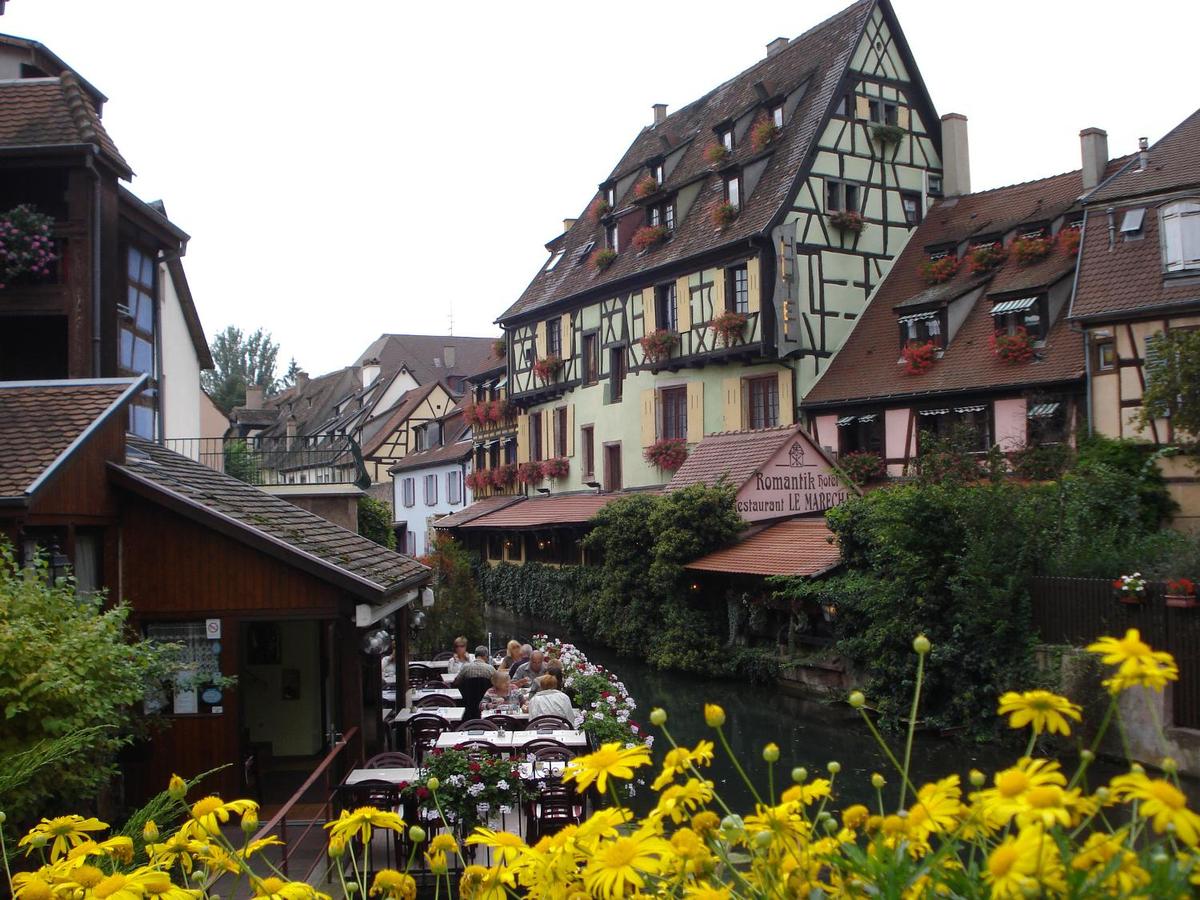

A cafe on a canal in Colmar. The town, situated on the Alsatian Wine Route, was founded in the 9th century. In 1226, it became a Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire. It was conquered by Louis XIV and the French in 1673 and over subsequent centuries alternated between German and French control. It reverted to France in 1945.
-
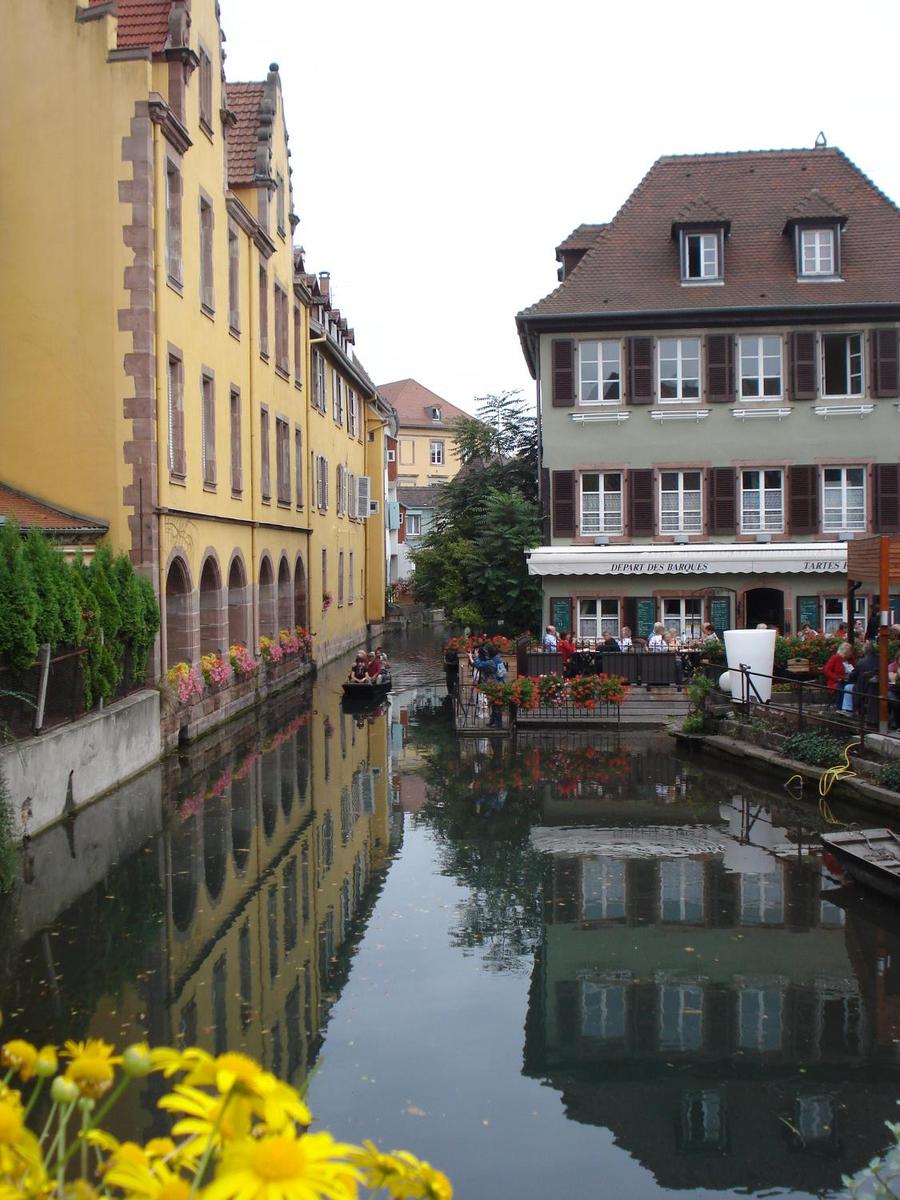

Buildings along a canal in Colmar, an Alsatian town known as "Little Venice." Situated on the Lauch River, Colmar connects to the Rhine via a canal.
-
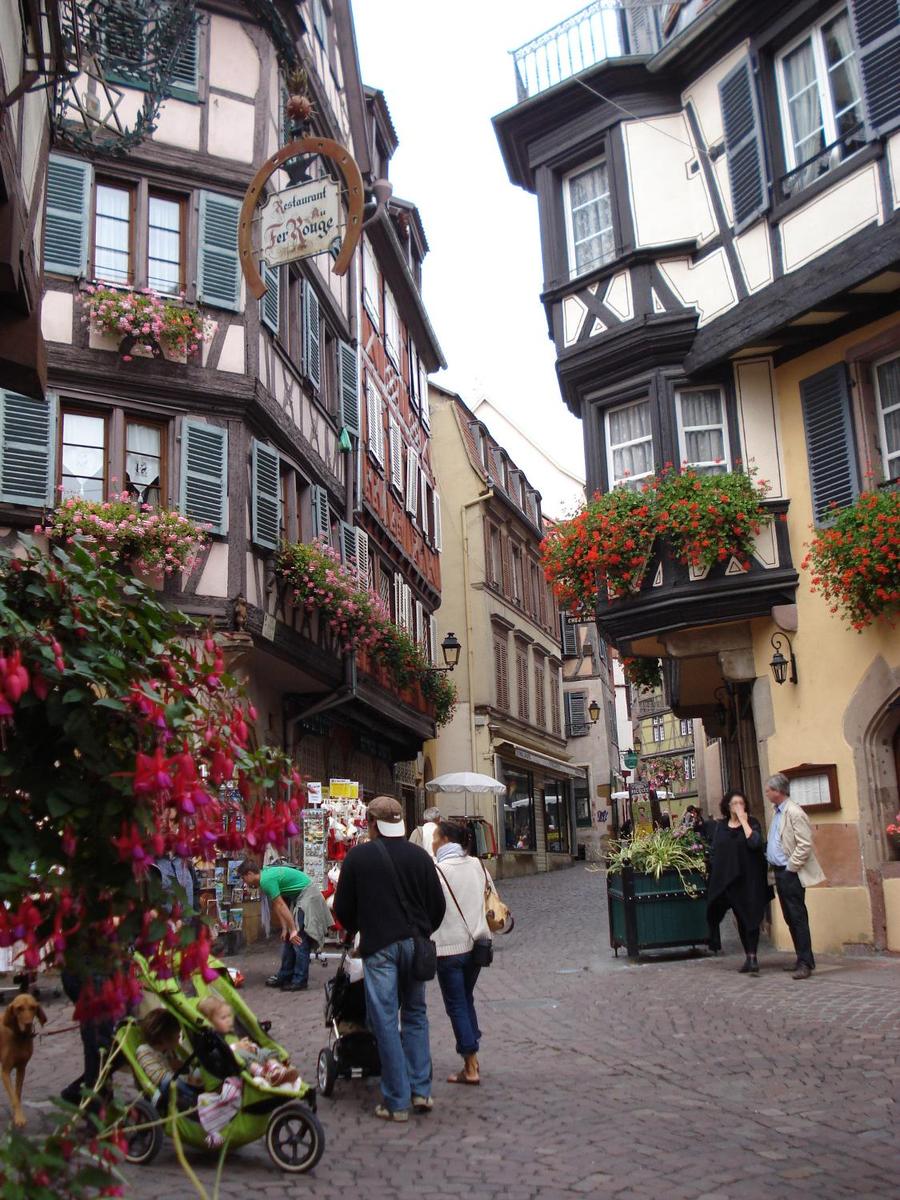

Half timbered houses along a shopping street in old Colmar.
-
A street scene in old Colmar. The picturesque town is a tourist magnet; it annually hosts the Alsatian Wine Fair.
-
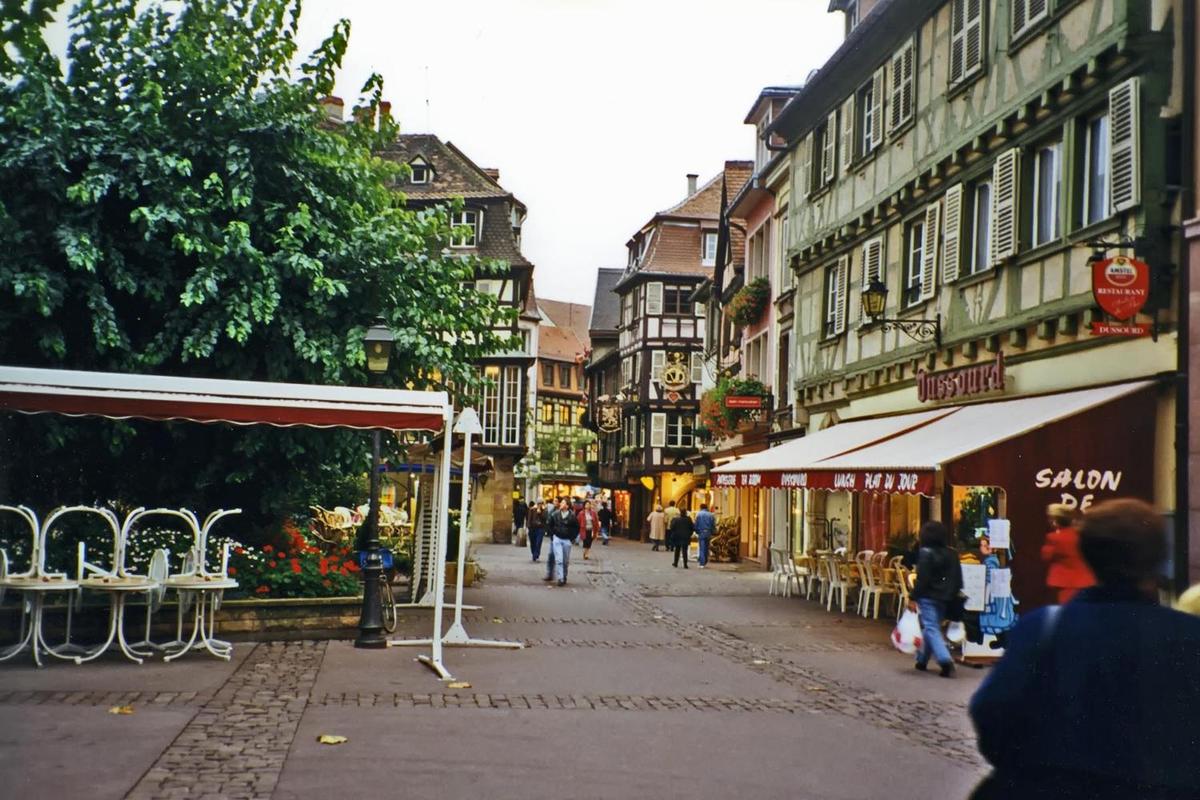

Street scene in the Alsatian town of Colmar.
-
Colorful houses along a canal in Colmar, an Alsatian town with the sobriquet of "Little Venice."
-
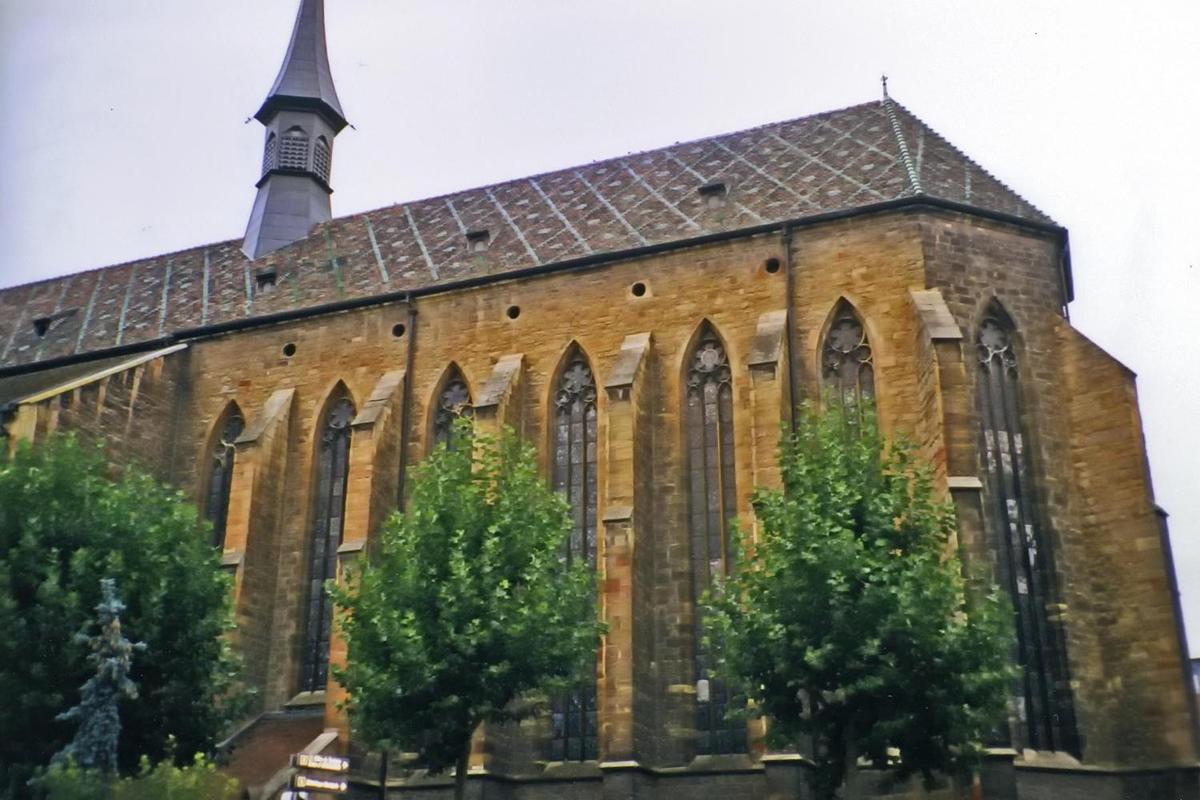

The Eglise Saint-Matthieu (Dominican Church of St. Matthew) in the Alsatian town of Colmar was built in the 13th century.
-
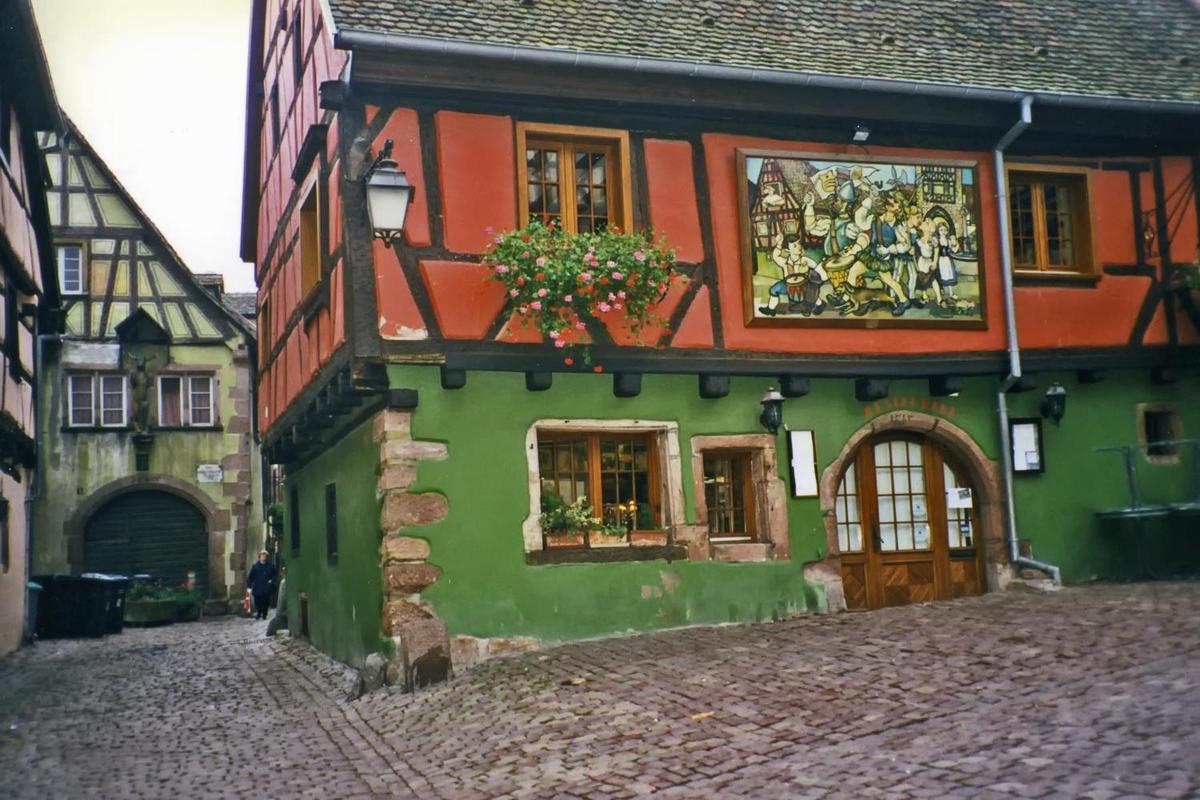

Colorful house in the medieval Alsatian town of Riquewihr. The locale is renowned not only for its historic architecture, but also for the fine wines it produces.
-
The road into Ingersheim on the Alsatian Wine Route.
-
{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Vineyards"},{"insert":" along the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Alsatian Wine Route"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
{"ops":[{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Vineyards"},{"insert":" along the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Alsatian Wine Route"},{"insert":".\n"}]}
-
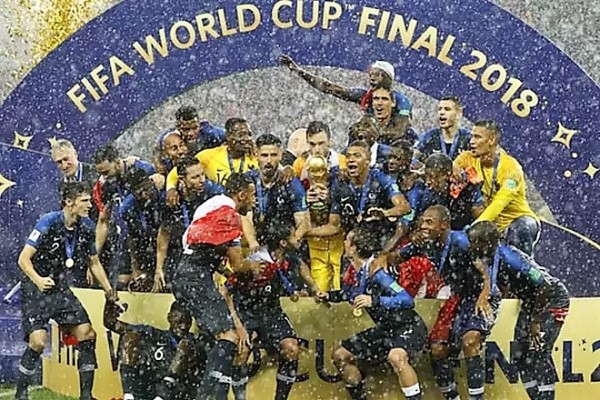

{"ops":[{"insert":"The "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"France national football"},{"insert":" (soccer)"},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":" team"},{"insert":" represents France in men's international football (soccer) and is controlled by the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"French Football Federation"},{"insert":", also known as FFF. The team's colors are blue, white, and red, and the coq gaulois its symbol. France is colloquially known as "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"Les Bleus (The Blues)"},{"insert":". They have won the World Cup finals in "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"1998 "},{"insert":"and "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"2018"},{"insert":". France plays their home matches at the Stade de France in Saint-Denis. In addition to the "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"two FIFA World Cups"},{"insert":", they have won two "},{"attributes":{"bold":true},"insert":"UEFA European Championships"},{"insert":", two FIFA Confederations Cups, one UEFA Cup of Champions and one UEFA Nations League title.\n"}]}
keyboard_arrow_up





